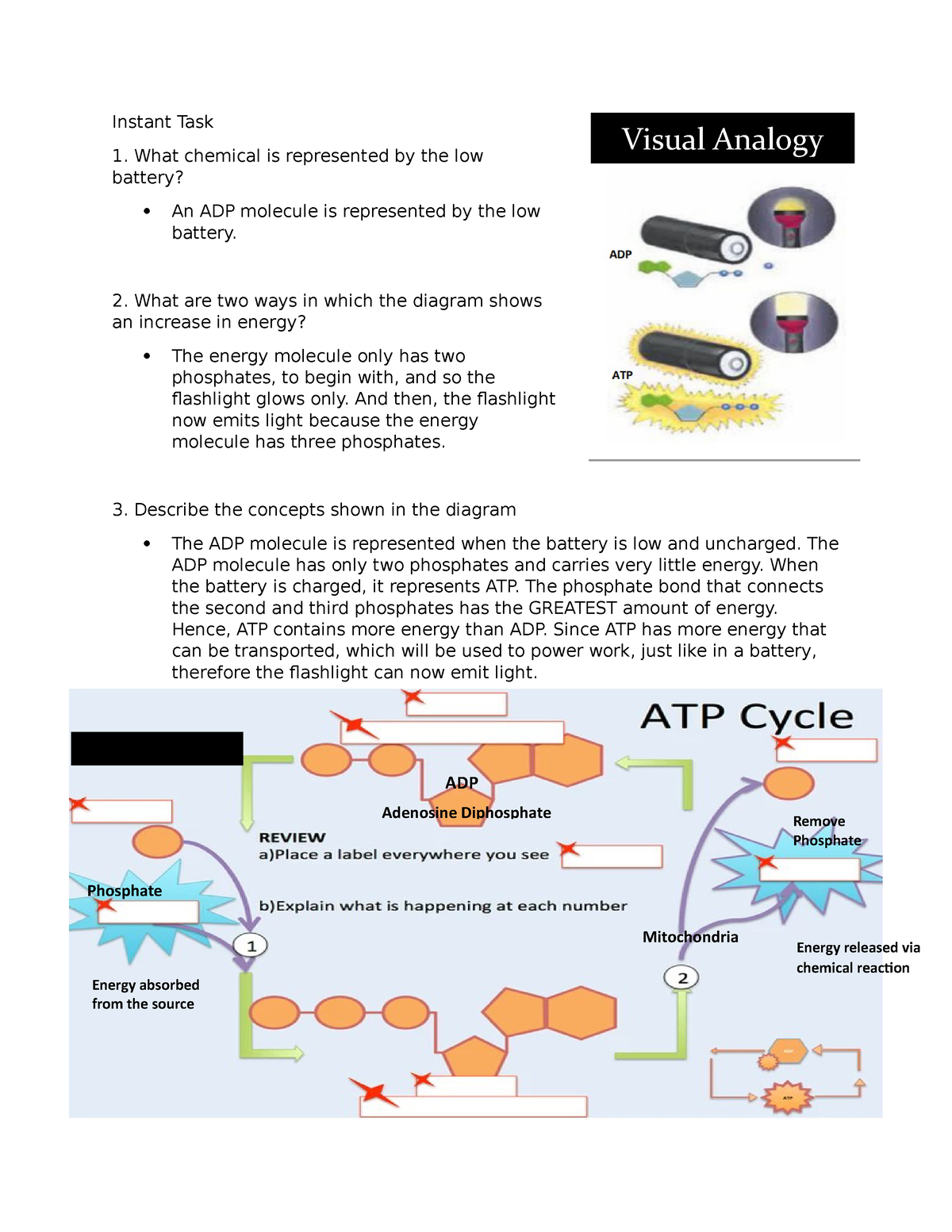
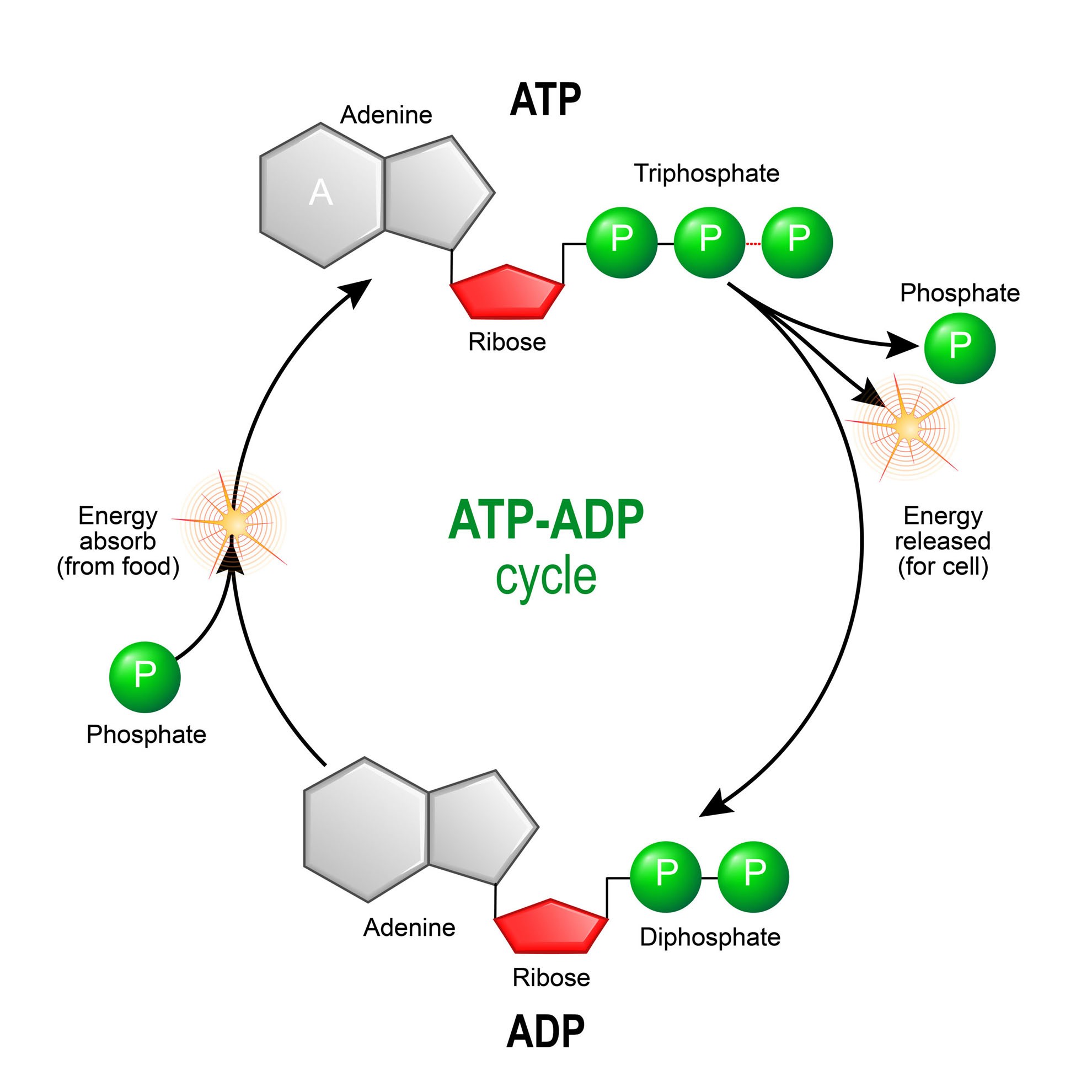
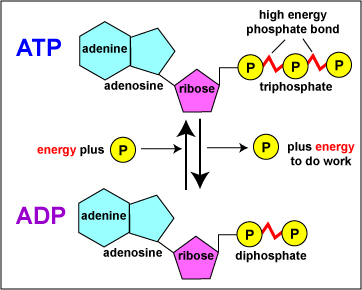
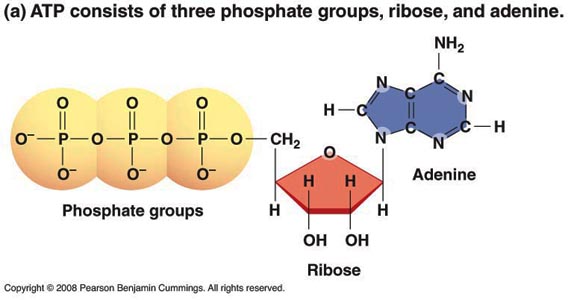
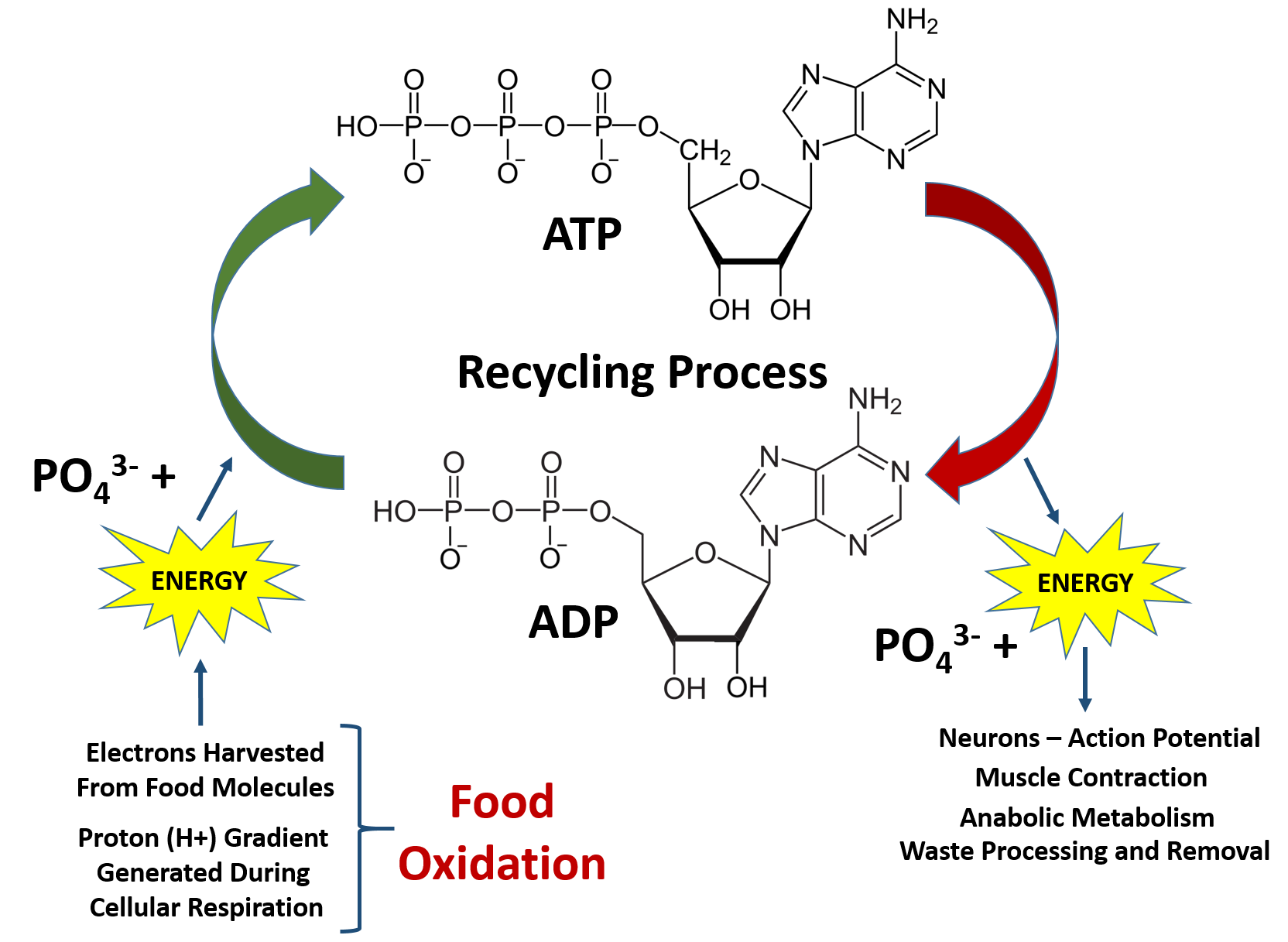
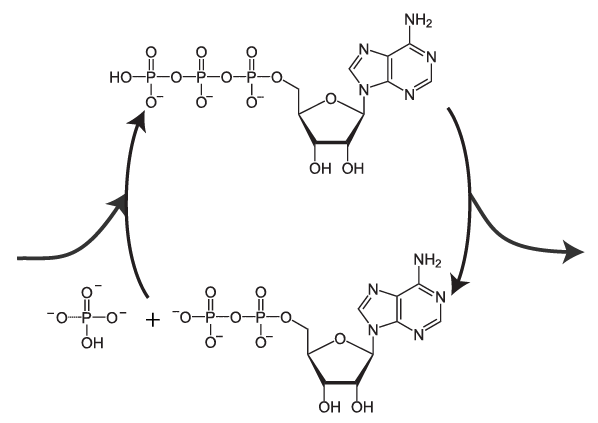
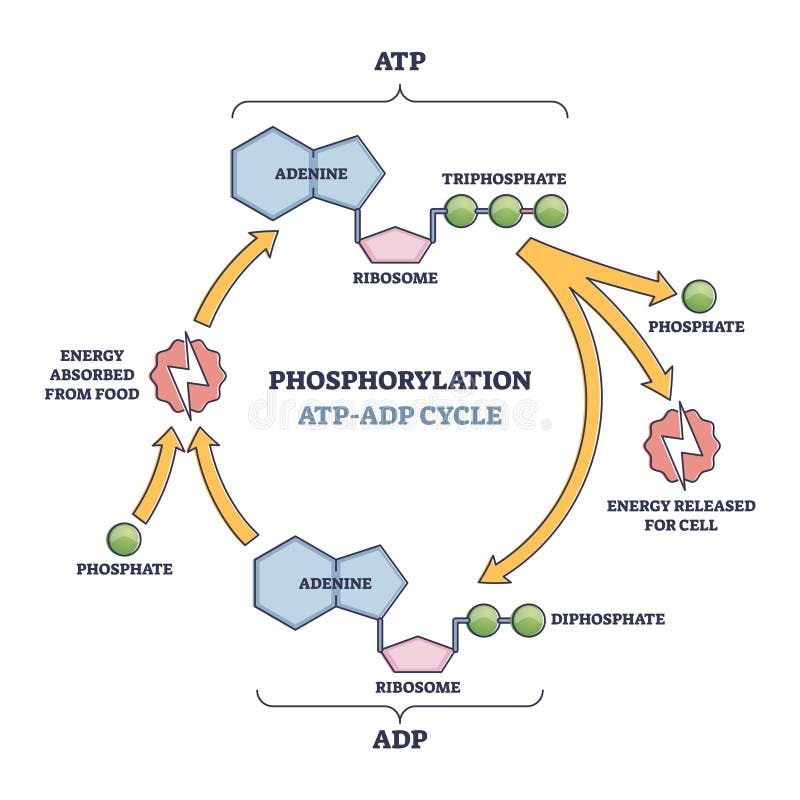
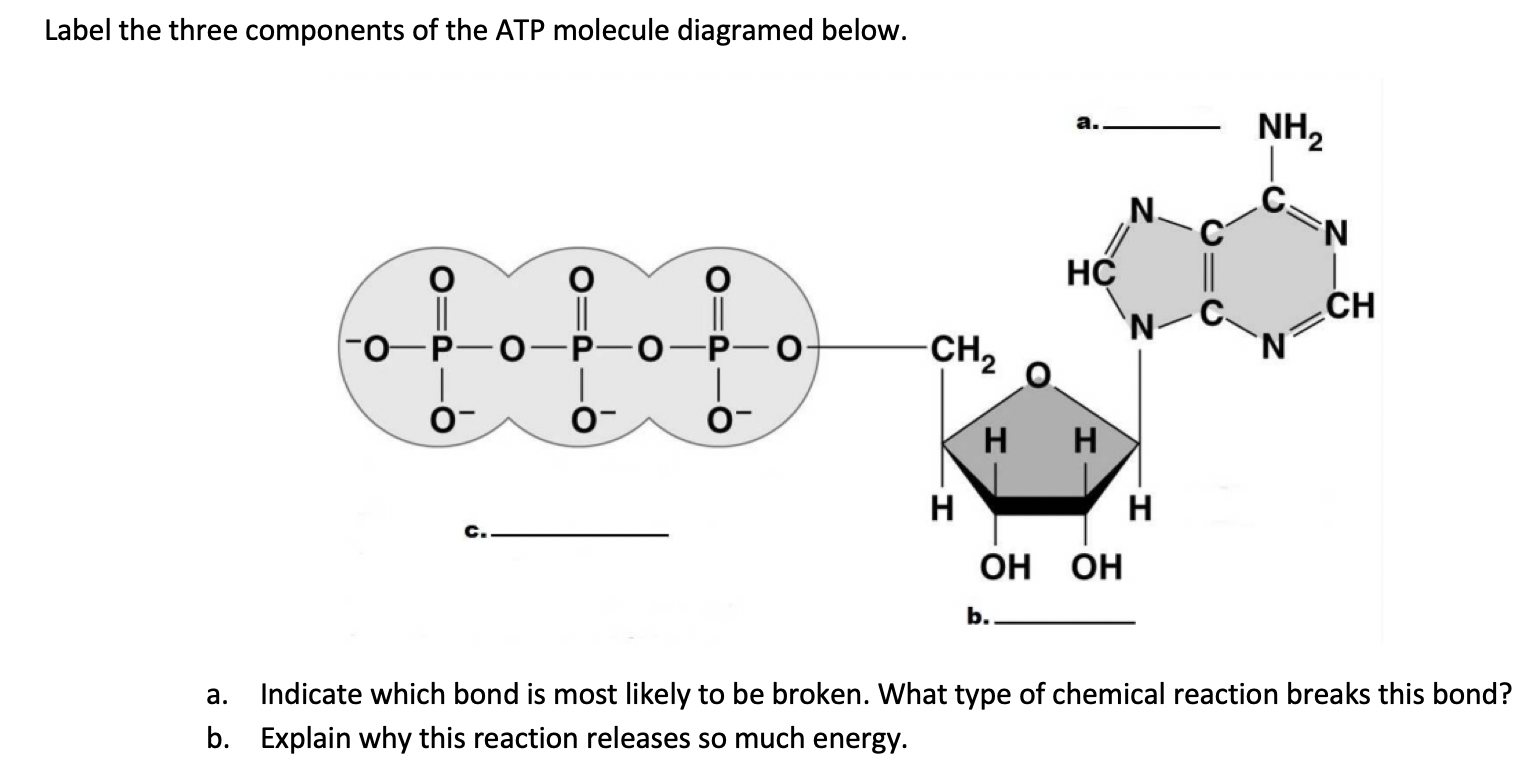
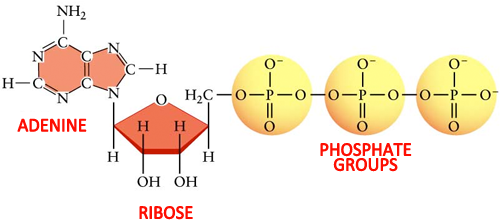
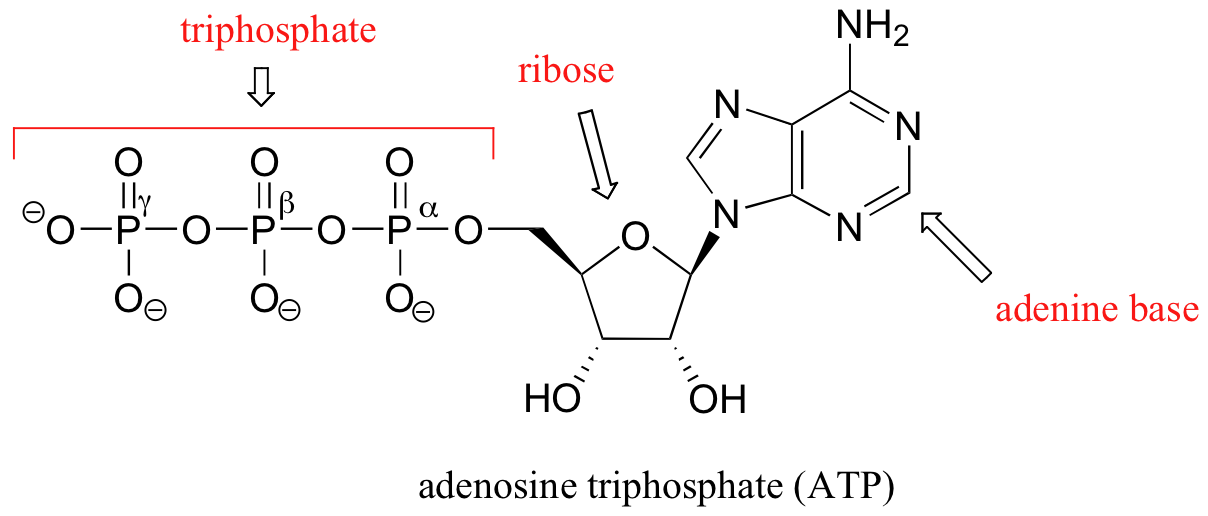
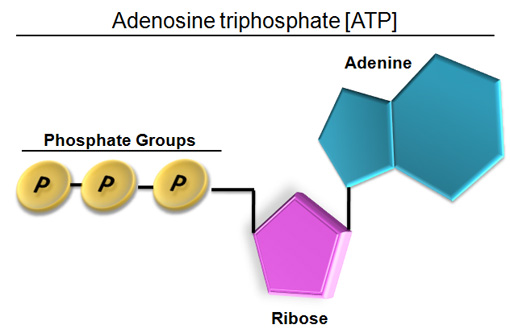
44 label atp and adp molecules
Where Does Glycolysis Occur? (A Guide) | OptimistMinds The total yield of this process is 2 NADH molecules and 4 ATP molecules, and there is a net gain of 2 NADH molecules and 2 ATP molecules from the glycolytic pathway per glucose. The next step is the enzymatic transfer of a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP by phosphoglycerate kinase, which in turn forms ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate. The Process By Which Food Is Burned To Release Energy There are two mechanisms of ATP synthesis: 1. oxidative phosphorylation, the process by which ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) that takes place in mitochondrion; and 2. substrate-level phosphorylation, in which ATP is synthesized through the transfer of high-energy phosphoryl groups from high-energy compounds to ADP.
Adverse Cardiac Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Another by-product of the cascade is the hypochlorite radical, formed by the conversion of hydrogen peroxide into hypochlorite ion by myeloperoxidase (MPO). 28 The free radicals destroy cell membranes and DNA, resulting in activation of poly(ADP) ribose and the exhaustion of intracellular ATP stores.

Label atp and adp molecules
Electron Transport System : Mechanism and Components | Turito Electron Transport System. The electron transport system, or ETS, is the metabolic mechanism of electron transport. Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce reduced coenzymes such as 10 molecules of NADH +, H + ions, 2 molecules of FADH 2, and 4 molecules of ATP. To liberate the energy held in these reduced coenzymes, they must be oxidized. What Happens When You Stop Taking Creatine? - SET FOR SET Known as adenosine triphosphate (triphosphate= 3 phosphates), ATP is the body's "energy currency" and is used to supply energy for a host of reactions, processes, and muscle contractions. During high-intensity activities such as lifting weights and HIIT workouts, the body requires ATP fast to fuel the muscles. File Type PDF Cellular Respiration Study Guide STUDY GUIDE Draw and label the parts in a mitochondrion and show where the different reactions happen. Write the chemical for- mula for cellular respiration in symbols and words. C6H12O6+6O2 (6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP) Microscopes offer a great way to discover an entire universe that lies beyond what we can see with the naked eye. From harmful
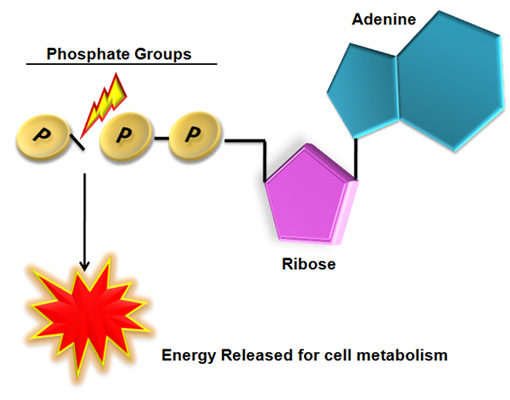
Label atp and adp molecules. Direct observation of the molecular mechanism underlying protein ... Incorporation of subunits into filaments triggers actin's adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity, causing the subunits to transition first into an adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-inorganic phosphate (P i) state and upon phosphate release to an ADP state ( 41, 42 ). BIOLOGY FORM TWO SUMMARIZED NOTES - Educationnewshub.co.ke ATP is synthesised from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate. The last bond connecting the phosphate group is a high-energy bond. Cellular activities depend directly on ATP as an energy source. When an ATP molecule is broken down, it yields energy. Process of Respiration . The breakdown of glucose takes place in many steps. Where Does The Energy Of Food Originally Come From Cells contain only a small amount of ATP at any one time. They create new ATP molecules from ADP as they need it using the energy stored in food (glucose) to add that third phosphate. Heterotrophs and Autotrophs The energy to make ATP from ADP comes from food (glucose). Where does most of the energy on Earth originate? The energy of the sun Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms What is the Difference Between Hydrogel and Silicone Hydrogel. The key difference between hydrogel and silicone hydrogel is that the lenses made of the hydrogel are less porous, whereas the lenses made of silicone hydrogel are a more porous type of soft contact lenses. Hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that cannot dissolve in water.
What do you understand by ATP and ADP for the Biology Portion of ... What is ATP and ADP? Cells capture and store the energy released in catabolic reactions through the use of chemical compounds known as energy carriers. The most significant example of an energy carrier is adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, which is formed when a simpler compound, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), combines with a phosphate group. Addressing the Problem in HCM: The Role of Cardiac Myosin ... - Medscape Medscape, LLC, encourages Authors to identify investigational products or off-label uses of products regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration, at first mention and where appropriate in the content. ... myosin head then forms a cross-bridge with actin that is necessary for myocyte contraction. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) breaks the ... Cancers | Free Full-Text | CC Chemokine Ligand-2: A Promising Target ... CC chemokine ligand-2 (CCL2), a proinflammatory chemokine that mediates chemotaxis of multiple immune cells, plays a crucial role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and promotes tumorigenesis and development. Recently, accumulating evidence has indicated that CCL2 contributes to the development of drug resistance to a broad spectrum of anticancer agents, including chemotherapy, hormone ... Emerging Therapies for Mitochondrial Disorders aicar. 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (aicar) is an adenosine monophosphate (amp) analogue (merrill et al., 1997) causing ampk to initiate catabolic mechanisms to produce atp and...
New articles: Biophysical Journal - Cell Crucial for mRNA-based vaccines are the composition, structure and properties of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) as their delivery vehicle. Using all-atom molecular dynamics simulations as a computational microscope, we provide an atomistic view on the structure of the Comirnaty vaccine LNP, its molecular organization, physico-chemical properties and insight in its pH-driven phase transition ... Gut and obesity/metabolic disease: Focus on microbiota metabolites ... When glucose internalized in islet β cells is metabolized, it results in elevation of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP):adenosine diphosphate (ADP) ratio, closure of ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels, and opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels (Ca 2+ channels), causing secretion of insulin. First, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs ... 16 Best Anti Aging Supplements in USA 2022 - Aesthetics Advisor Here are the best supplements with anti-aging properties. 1. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is needed to make NAD+. NAD+ is a very important substance in the cells. It provides energy for cells and is also a cofactor for proteins that repair and maintain our epigenome and our DNA. Difference Between Photosynthesis and Respiration Both involve a series of biochemical reactions and use and produce the same energy, which is ATP. They both use the same eco enzymes that are NADP and NAD. Both reactions complement each other in the environment. Although there are a lot of differences between these two biological reactions, they both cannot happen without one another.
Frontiers | The multifaceted roles of ER and Golgi in metabolic ... The IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the UPR is also a critical regulator of metabolic-stress-induced lipid disequilibrium ().Adipocyte Xbp1s overexpression prevents obesity in HFD-fed mice and leptin-deficient ob/ob mice via increased uridine biosynthesis ().Added to this, ectopic adipocyte Xbp1s expression promotes systemic glucose homeostasis in both lean and ob/ob mice by increasing adiponectin serum ...
BIOLOGY FORM ONE SUMMARIZED NOTES - Educationnewshub.co.ke In the synthesis of a lipid, three fatty acid molecules combine with one glycerol molecule to form a triglyceride. Three molecules of water are lost in the process. This is a condensation reaction and water is given off. Lipids are hydrolysed e.g. during digestion to fatty acids and glycerol, water is added.
Mitochondrion - Wikipedia A mitochondrion (/ ˌ m aɪ t ə ˈ k ɒ n d r i ə n /; pl. mitochondria) is a double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Mitochondria use aerobic respiration to generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is subsequently used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the ...
Organelle - Genome.gov Definition. An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
Analytical chemistry | Nature Communications A facile way to construct sensor array library via supramolecular chemistry for discriminating complex systems. The development of sensor unit libraries that require minimal synthetic effort is ...
Novel Treatments for Hyperglycemia - Medscape GK catalyzes the conversion of glucose plus ATP to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) plus ADP. HK 1-3 have a high affinity for glucose, between 0.03 and 0.2 mM/L, and obey Michaelis-Menten kinetics, while the affinity of GK is in the physiologic glucose range, between 5 and 12 mM/L, allowing it to function as a glucose sensor.
Enzyme Deficiency: Symptoms And Treatment - This Nutrition "Synthetase" is added to the name of the enzymes of this group - ATP synthetase catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate. Isomerases catalyze isomerization reactions. As we have already found out, the vast majority of enzymes are proteins.
Cyclic ADP ribose isomers: Production, chemical structures, and immune ... Cyclic ADP ribose (cADPR) isomers are signaling molecules produced by bacterial and plant Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domains via NAD + hydrolysis. We show that v-cADPR (2′cADPR) and v2-cADPR (3′cADPR) isomers are cyclized by O-glycosidic bond formation between the ribose moieties in ADPR.Structures of 2′cADPR-producing TIR domains reveal conformational changes leading to an active ...
Photosynthesis - Wikipedia Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities.Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water - hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek ...
Biology | Free Full-Text | Fossil Biomarkers and Biosignatures ... ADP = adenosine diphosphate; ATP = adenosine triphosphate. ( B ) Discriminant vector arrows for tissue categories (black, n = 5) and functional groups ( n = 53 extracted relative intensities) in the Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) shown in Figure 4 A. Functional groups are colour-coded (corresponding to functional group labels in ( A ...
File Type PDF Cellular Respiration Study Guide STUDY GUIDE Draw and label the parts in a mitochondrion and show where the different reactions happen. Write the chemical for- mula for cellular respiration in symbols and words. C6H12O6+6O2 (6CO2+6H2O+Energy (ATP) Microscopes offer a great way to discover an entire universe that lies beyond what we can see with the naked eye. From harmful
What Happens When You Stop Taking Creatine? - SET FOR SET Known as adenosine triphosphate (triphosphate= 3 phosphates), ATP is the body's "energy currency" and is used to supply energy for a host of reactions, processes, and muscle contractions. During high-intensity activities such as lifting weights and HIIT workouts, the body requires ATP fast to fuel the muscles.
Electron Transport System : Mechanism and Components | Turito Electron Transport System. The electron transport system, or ETS, is the metabolic mechanism of electron transport. Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce reduced coenzymes such as 10 molecules of NADH +, H + ions, 2 molecules of FADH 2, and 4 molecules of ATP. To liberate the energy held in these reduced coenzymes, they must be oxidized.
.jpg)


















Post a Comment for "44 label atp and adp molecules"