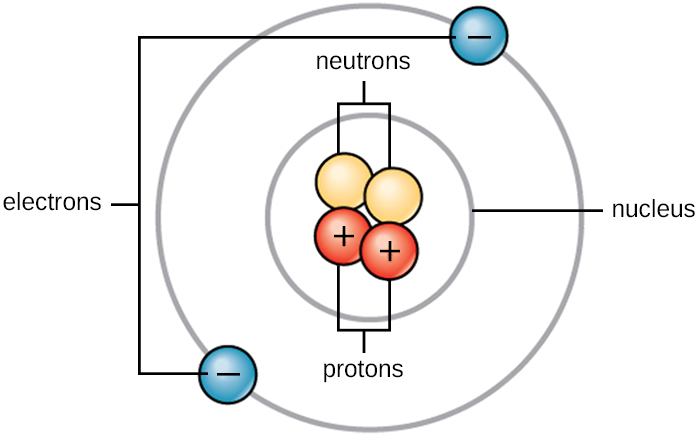
38 parts of a helium atom
Wave function for a helium atom | Physics Forums For helium, you should be doing the same, namely first rewrite the Hamiltonian in the center-of-mass frame, then look for solutions in terms of the relative coordinates. Note also that the label "proton" is not appropriate for helium, but should rather be "nucleus." Oct 10, 2019 #3 Gold Member 507 32 DrClaude said: Helium Isotopes, Radioactive Decay and Half-Life - ThoughtCo Helium has seven known isotopes, ranging from He-3 to He-9. Most of these isotopes have multiple decay schemes where the decay type depends on the overall energy of the nucleus and its total angular momentum quantum number. This table lists helium isotopes, half-life, and type of decay: p proton emission n neutron emission α alpha decay
Recombination (cosmology) - Wikipedia Primordial helium recombination. Helium nuclei are produced during Big Bang nucleosynthesis, and make up about 24% of the total mass of baryonic matter. The ionization energy of helium is larger than that of hydrogen and it therefore recombines earlier. Because neutral helium carries two electrons, its recombination proceeds in two steps.
Parts of a helium atom
Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in an Atom 02/06/2019 · Each atom has an integer number of neutrons, but the periodic table gives a decimal value because it is a weighted average of the number of neutrons in the isotopes of each element. So, what you need to do is round the atomic weight to the nearest whole number to get a mass number for your calculations. For hydrogen, 1.008 is closer to 1 than 2, so let's call it 1. Loading... - BrainPop Loading... - BrainPop ... Loading... Chemical elements listed by atomic number - Lenntech Chemical elements listed by atomic number The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number. click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
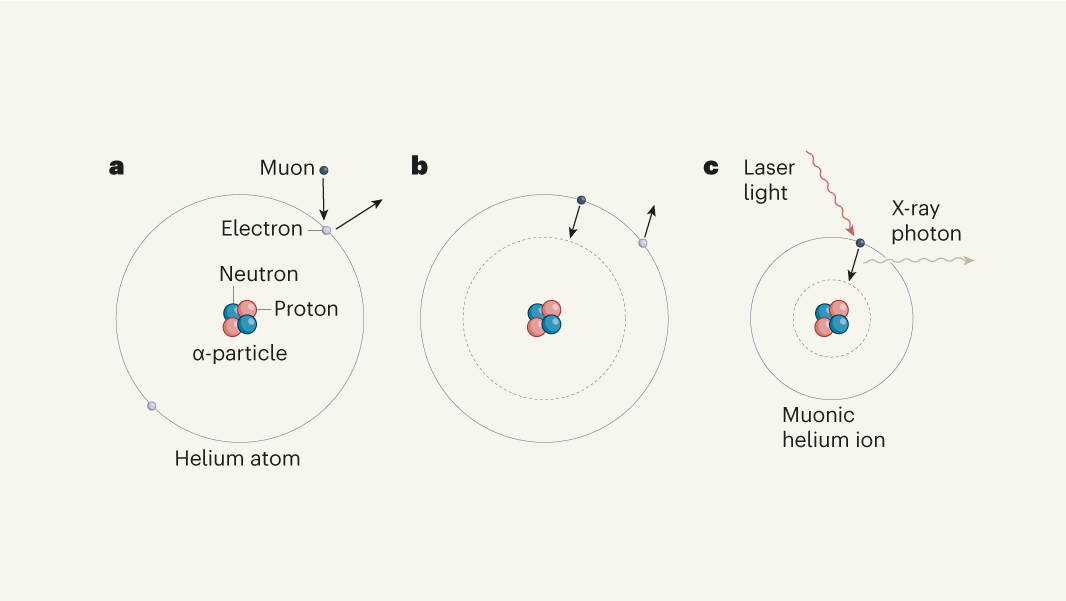
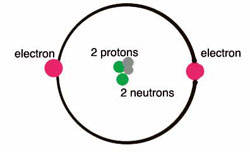
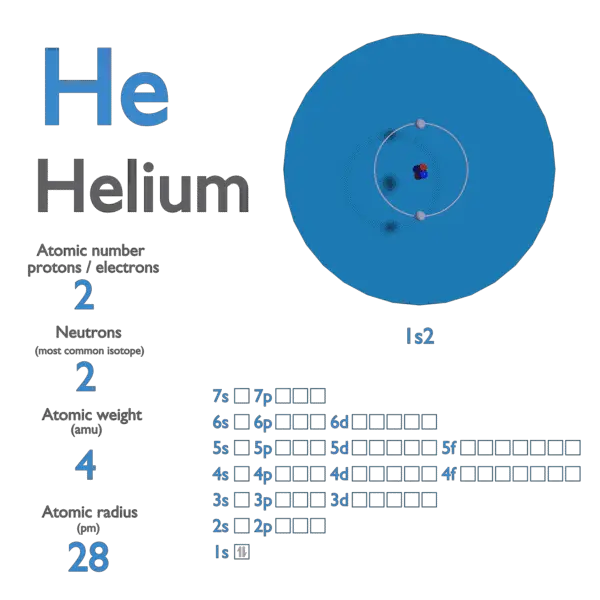
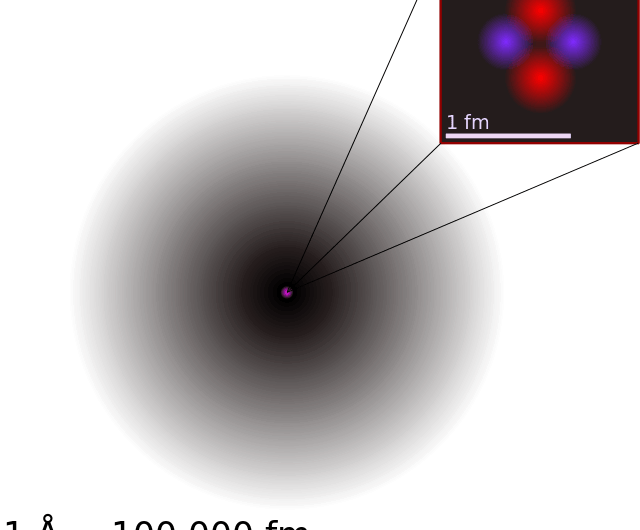
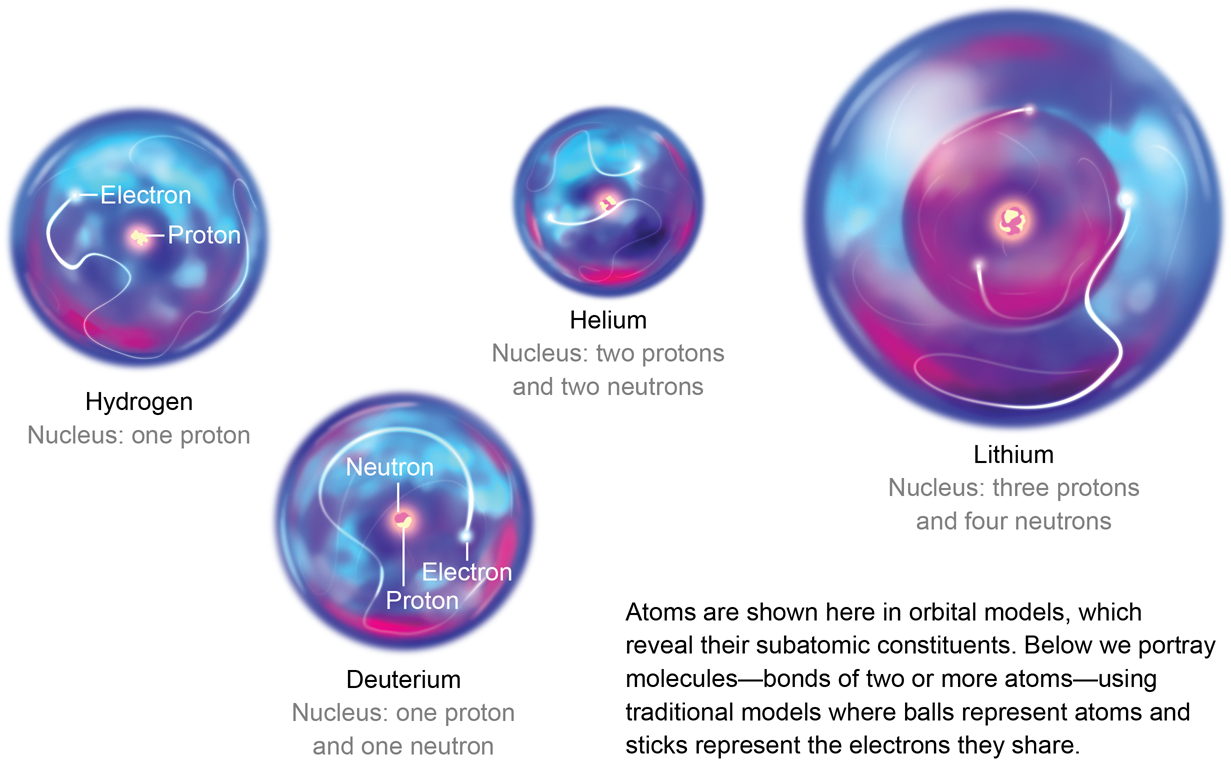
Parts of a helium atom. Helium-4 - Wikipedia In an experiment involving the use of exotic helium atoms where an atomic electron was replaced by a muon, the nucleus size has been estimated to be 1.67824(83) fm. Stability of the 4 He nucleus and electron shell. The nucleus of the helium-4 atom is identical to an alpha particle. Atomic Design Methodology | Atomic Design by Brad Frost Each atom in the natural world has its own unique properties. A hydrogen atom contains one electron, while a helium atom contains two. These intrinsic chemical properties have profound effects on their application (for example, the Hindenburg explosion was so catastrophic because the airship was filled with extremely flammable hydrogen gas versus inert helium gas). In the … Recombination (cosmology) - Wikipedia In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch during which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms.Recombination occurred about 370,000 years after the Big Bang (at a redshift of z = 1100).The word "recombination" is misleading, since the Big Bang theory doesn't posit that protons and electrons had been … Helium - Periodic Table Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons.
What is Helium - Properties of Helium Element - Nuclear Power What is Helium. Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas, the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among ... Helium Atom - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics There are four possible states for the helium atom: where the S and P refer, respectively, to the total orbital angular momentum of the two electrons and the leading superscript 1 or 3 uses the multiplicity 2 S + 1 to designate the total spin. The states are referred to, respectively, as singlet and triplet states. Helium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table Helium can be found in certain parts of the world, notably in Texas, as a minor component in some sources of natural gas. The interesting thing is how this gas gets into the ground in the first place. Unlike virtually every other atom around us, each atom of … Build an Atom - Atoms | Atomic Structure | Isotope Symbols ... Build an atom out of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and see how the element, charge, and mass change. Then play a game to test your ideas!
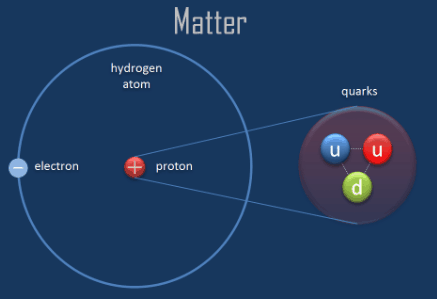
Parts of an Atom: Overview & Structure | What is an Atom? - Video ... Noble gases include neon, argon, and helium. At the opposite end of the spectrum, the alkali metals are in group one. They have only a single electron in their outermost electron shell and are ... Helium Atom - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics There are four possible states for the helium atom: where the S and P refer, respectively, to the total orbital angular momentum of the two electrons and the leading superscript 1 or 3 uses the multiplicity 2 S + 1 to designate the total spin. The states are referred to, respectively, as singlet and triplet states. Helium - Atomic Mass - Atomic Weight - He - Periodic Table 21/11/2020 · Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Its monatomic form (H) is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe, constituting … Helium Atom - University of Texas at Austin Helium Atom A helium atom consists of a nucleus of charge surrounded by two electrons. Let us attempt to calculate its ground-state energy. Let the nucleus lie at the origin of our coordinate system, and let the position vectors of the two electrons be and , respectively. The Hamiltonian of the system thus takes the form (1180)
Loading... Loading... ... Loading...
What Are The Parts Of An Atom? - Universe Today Our current model of the atom can be broken down into three constituents parts - protons, neutron, and electrons. Each of these parts has an associated charge, with protons carrying a positive...
What is an Atom | What Does An Atom Look Like? - Video ... Nov 10, 2021 · The element helium, for example, contains atoms with two protons in the nucleus. The element iron contains atoms with 26 protons. ... Separate the three parts of an atom and explain each ...
Build An Atom - Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education After this activity, the student will be able to describe the basic structure of matter, name the parts of an atom, have experience using the Periodic Table, explain elements, and have the background to understand isotopes. ... General questions about the properties of elements assume standard temperature and pressure (helium is liquid below ...
Atom Quiz - ThoughtCo Mar 08, 2017 · The atomic number of an atom is the same as the number of protons it has. For example, hydrogen has one proton and is atomic number 1. For example, hydrogen has one proton and is atomic number 1. Each helium atom has two protons, so the element is atomic number 2.
The helium atom (Chapter 14) - Atoms and Molecules Interacting with Light Summary Introduction Helium is the natural connection between the hydrogen-like atoms (one electron outside a spherical core, such as the alkali-metal atoms of Chap. 10) and all the others in the periodic table. For these one-electron atoms the field-free description of the electron motion in terms of three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m suffices.
How many subatomic particles does helium have? - Answers The nucleus of a helium atom contains four subatomic particles how many neutrons does the helium atom have? Helium has two neutrons and two protons in its nucleus. ... What is the smallest part of ...
The Element Helium -- Helium Atom Helium is a colorless, odorless, tasteless chemical element, one of the noble gases of the periodic table of elements. Its boiling and melting points are the lowest among the elements; except in extreme conditions, it exists only as a gas. The second most abundant element in the universe, significant amounts are found on Earth only in natural ...
Helium-4 - Wikipedia The helium atom is the second simplest atom (hydrogen is the simplest), but the extra electron introduces a third "body", so the solution to its wave equation becomes a "three-body problem", which has no analytic solution.However, numerical approximations of the equations of quantum mechanics have given a good estimate of the key atomic properties of helium-4, such as its …
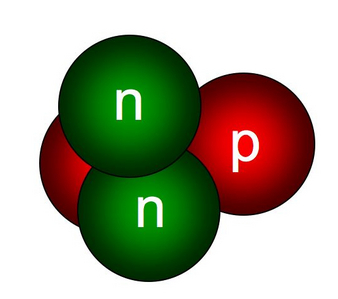
GMS: The Helium Atom Helium nuclei were created in the Big Bang and contain two protons and two neutrons each. Helium is the second most abundant element, comprising roughly one quarter of the mass of the Universe. This animation zooms into a standard helium atom, showing its protons (green), neutrons (white), and electrons (blue). Download Options
Chemistry for Kids: Elements - Helium - Ducksters Kids learn about the element helium and its chemistry including atomic weight, atom, uses, sources, name, and discovery. Plus properties and characteristics of helium. ... new helium is created in the center of stars and also as part of radioactive decay on Earth. Helium from radioactive decay can be found trapped underground in natural gas ...
The Helium Atom - University of California, San Diego The Helium Atom The Hamiltonian for Helium has the same terms as Hydrogen but has a large perturbation due to the repulsion between the two electrons. Note that the perturbation due to the repulsion between the two electrons is about the same size as the the rest of the Hamiltonian so first order perturbation theory is unlikely to be accurate.
Helium - Element information, properties and uses | Periodic ... After hydrogen, helium is the second most abundant element in the universe. It is present in all stars. It was, and is still being, formed from alpha-particle decay of radioactive elements in the Earth. Some of the helium formed escapes into the atmosphere, which contains about 5 parts per million by volume.
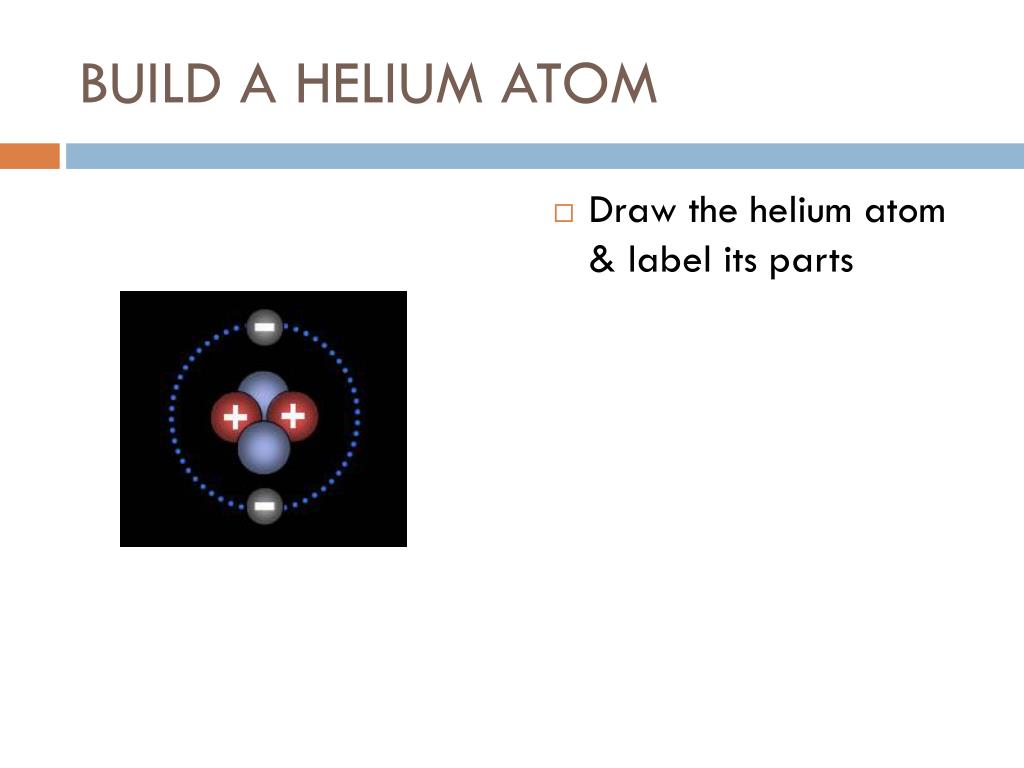
Atomic Structure Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Atomic Structure Quiz. Draw and Label the parts of a helium atom. Include the mass and charge of each subatomic particle. Should have two protons and two neutrons and 2 electrons and an electron cloud. protons: +, 1 amu neutrons: 0, 1 amu electrons: -1, 1/1840 amu.
GMS: The Helium Atom - NASA The Helium Atom. Released on July 3, 2007. Helium nuclei were created in the Big Bang and contain two protons and two neutrons each. Helium is the second most abundant element, comprising roughly one quarter of the mass of the Universe. This animation zooms into a standard helium atom, showing its protons (green), neutrons (white), and ...
Helium atom | definition of Helium atom by Medical dictionary helium. (He) [ he´le-um] a chemical element, atomic number 2, atomic weight 4.003. (See Appendix 6.) Helium is a chemically inert element that is odorless, tasteless, and noncombustible. Because of its low density it is easily moved through the air passages and therefore requires little effort in breathing on the part of the patient in ...
Helium atom - Wikipedia Helium is composed of two electrons bound by the electromagnetic force to a nucleus containing two protons along with either one or two neutrons, depending on the isotope, held together by the strong force. Unlike for hydrogen, a closed-form solution to the Schrödinger equation for the helium atom has not been found.
What is an Atom | What Does An Atom Look Like? - Study.com 10/11/2021 · Composition of an Atom. Structurally, atoms are made of a small dense nucleus and a larger electron cloud. The nucleus of an atom is much smaller than the electron cloud.An electron cloud's radius ...
Atom Quiz - ThoughtCo 08/03/2017 · Scientists Building Atom. Paper Boat Creative, Getty Images You have the right stuff to eventually become a scientist or teacher. You know what an atom is and understand the basics of how they work, but there are gaps in your knowledge. The next step? Fill in the gaps or take another educational quiz.
PDF 24. The Helium Atom - Weber State University ground state and the two lowest excited states of helium. To put these results into context, please look at the energy level diagram in Section 5.2.1 of Gri ths. This truncated-matrix approach to the helium atom, including the Mathematica code that I'll show in class, is based on a recent article by Robert C. Mass e and
helium | Definition, Properties, Uses, & Facts | Britannica Ordinary air contains about 5 parts per million of helium, and Earth's crust is only about 8 parts per billion. The nucleus of every helium atom contains two protons, but, as is the case with all elements, isotopes of helium exist. The known isotopes of helium contain from one to six neutrons, so their mass numbers range from three to eight.
Helium Energy Levels - GSU Helium Energy Levels The helium ground state consists of two identical 1s electrons. The energy required to remove one of them is the highest ionization energy of any atom in the periodic table: 24.6 electron volts. The energy required to remove the second electron is 54.4 eV, as would be expected by modeling it after the hydrogen energy levels.The He+ ion is just like a hydrogen atom with two ...
Helium - Wikipedia Helium (from Greek: ἥλιος, romanized: helios, lit. 'sun') is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements.It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the ...
Which part of a helium atom is positively charged? - Answers Which part of a helium atom is positively charged? the nucleus contains protons (positive) and neutrons (neutral). The nucleus is always the positively charged, dense center of an atom.
Helium (He) - Physical & Chemical Properties, Uses, Isotopes - BYJUS Helium falls under inert gas since its outermost electron orbital is full of two electrons. Helium can also be found in lasers, compressed air tanks and coolant in nuclear reactors. It holds the lowest boiling and melting points amongst all other elements. Nuclear fusion of hydrogen in stars generates a significant amount of helium. Isotopes
Helium - Protons - Neutrons - Electrons - Electron Configuration Protons and Neutrons in Helium. Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z.The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
Chemical elements listed by atomic number - Lenntech Chemical elements listed by atomic number The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number. click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
Loading... - BrainPop Loading... - BrainPop ... Loading...
Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in an Atom 02/06/2019 · Each atom has an integer number of neutrons, but the periodic table gives a decimal value because it is a weighted average of the number of neutrons in the isotopes of each element. So, what you need to do is round the atomic weight to the nearest whole number to get a mass number for your calculations. For hydrogen, 1.008 is closer to 1 than 2, so let's call it 1.





















Post a Comment for "38 parts of a helium atom"