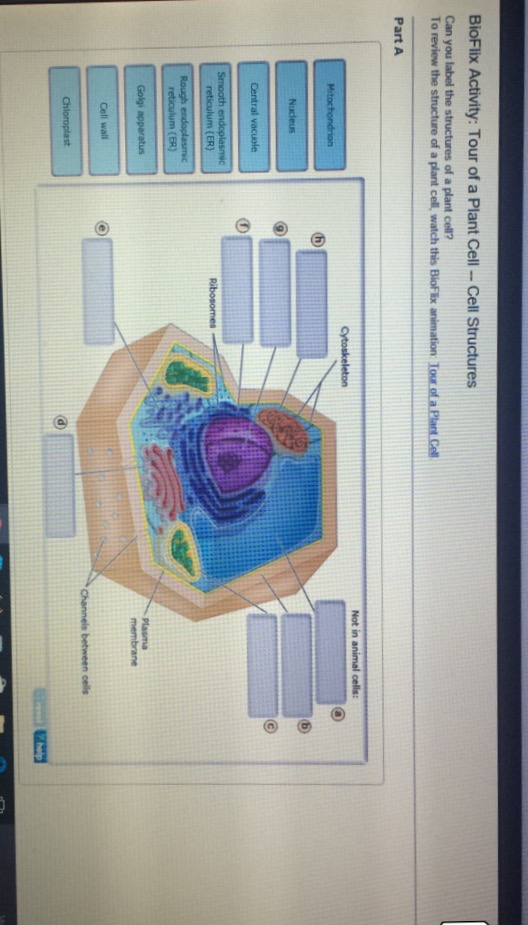
42 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
PDF Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells - Grosse Pointe Public Schools The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 - How Is a Cell Like a Factory? Part of factory Cell organelle Function Control ... Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure & Function (with ... - Sciencing Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. Eukaryotic cells also have organelles, which are membrane-bound structures found within the cell.
bio Flashcards - Quizlet Classify each statement as a description of prokaryotic cells or eukaryotic cells. A generalized prokaryotic cell and a generalized eukaryotic cell are shown. ... Label each part with the correct component molecule. Only two molecule names will be placed. ... For each example, identify if the food contains mostly saturated or unsaturated fatty ...
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
Biology - Chapter 3 Mastering HW Assignment Flashcards & Practice Test ... The round body that sits inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and ribosomal RNA is known as the nucleolus. 7. Chromosomes are tightly coiled bundles of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells. Select the cellular structure that can be found in both plant and animal cells. Mitochondria Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells - Windows to the Universe The "brains" of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria. Make energy out of food. Ribosomes. Make protein. Golgi Apparatus. Make, process and package proteins. Lysosome. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down. Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe May 12, 2022 · A eukaryotic cell is an advanced type of cell that has a well-defined nucleus and multiple membrane-bound organelles. DNA is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration.
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.. BYJUS BYJUS PDF Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Bellarmine University and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56 Solved: Label the following parts of this eukaryotic cell ... Membrane is a structural component that separates intracellular and extracellular environment by means of plasma membrane. Inside the eukaryotic cell (nucleus having), numerous cell organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus, etc. are present, which serve various functions. Important Parts of Eukaryotic Cells - dummies All eukaryotic cells have organelles, a nucleus, and many internal membranes. These components divide the eukaryotic cell into sections, with each specializing in different functions. Each function is vital to the cell's life. The plasma membrane is made of phospholipids and protein and serves as the selective boundary of the cell.
Label Eukaryotic Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Label Eukaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Eukaryotic Cells: Types and Structure (With Diagram) 1. Undifferentiated Cells: ADVERTISEMENTS: These unspecialized cells are capable of undergoing division and development. For example, Zygote, stem cells (in animals) and meristematic cells (in plants) 2. Differentiated cells (- Post-mitotic cells): These are specialized cells which perform a specific function and exhibit division of labour. Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Diagram - Quizlet Nuclear Envelope ... Nucleus ... Chromatin ... Nucleus ... Ribosomes ... Golgi Apparatus ... Lysosome ... Mitochondira ... Peroxisome ... Microvilli ... Microtubules ... Intermediate Filaments ... Microfilaments ... Cytoskeleton ... Centrosome ... Cell Organelles - Types, Structure and their Functions - BYJUS Single membrane-bound organelles: Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell. Double membrane-bound organelles: Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles present only in a eukaryotic cell.
Solved Can you identify the cellular structures and their - Chegg Then identify the function of each organelle on the blue target below it. Resat Help Golg plasma Request Answer rovide Feedback Next > Question: Can you identify the cellular structures and their functions in this diagram of a eukaryotic cell? ? Part A Drag the organelle labels to the appropriate pink targets. Eukaryotic Cells - Biology 2e Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.". Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions Flashcards - Quizlet eukaryote/eukaryotic cells with membrane-bound nucleus nucleus region of eukaryotic cells that controls activities of cells; contains chromosomes (DNA) and nucleolus; filled with nucleoplasm cytoskeleton keeps cell from collapsing plastids structures in the cytoplasm of plant cells that contain pigments (chloroplasts, amyloplasts, chromoplasts)
identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell Advertisement Answer 2 rawan12343 can you take a picture so I can help you identify it. Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. yes the nucleus would be your answer. Advertisement Answer 5.0 /5 5 jenniferlove131418 Answer: Label A nucleus Label B cytoplasm Label C ribosomes Label D
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes - Kenhub The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram The plant cell, being a eukaryotic cell, has large complex ribosomes with higher S units, with four rRNAs with over 80 proteins. The large subunit has the S unit of the 60s (28s rRNA, 5.8s rRNA, and 5s rRNA) with 42 proteins. The small subunit has a sedimentation rate of the 40s, made up one rRNA and 33 proteins.
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - P2 Parts of the Eukaryotic Endomembrane System Nucleus: The nucleus is typically the largest and most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell. Bound by a double-layer nuclear membrane, the nucleus contains the cell's genome—the main genetic instructions in the form of DNA ( deoxyribonucleic acid ).
identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Sep 10, 2020 · Identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell. 1. See answer. plus. plus. Add answer + 5 pts. report flag outlined. report flag outlined. bell outlined.
[Solved] identify and label each part of this Eukaryotic cell ... identify and label each part of this Eukaryotic cell Biology Science cell biology Comments (1) Answer & Explanation Solved by verified expert All tutors are evaluated by Course Hero as an expert in their subject area. Cell wall. Plasma membrane. Nucleus. Golgi apparatus. Ribosomes. Cytoplasm. Mitochondria. Endoplasmic reticulum. Central vacuole.
Eukaryotic Cells - Visible Body Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus —an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope —where DNA is stored. There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such as human red blood cells, which don't have a nucleus when mature.
3.3 Eukaryotic Cells - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly.


Post a Comment for "42 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell."